Engineering and Design
Layout Drawing with Power Outlets
- Layout Drawing: Creating a scaled plan of the building, showing the location of all electrical components, including walls, doors, windows, and furniture.
- Power Outlets: Indicating the exact placement and type of power outlets required for specific appliances and equipment in each room.
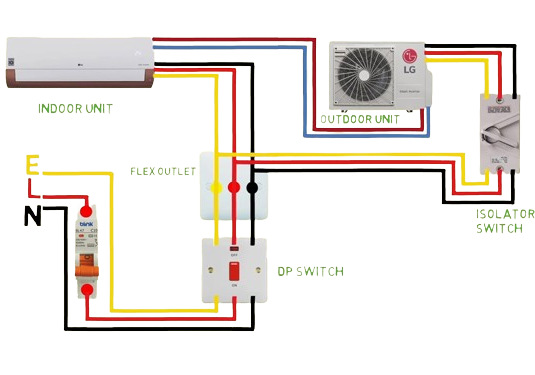
Load Calculations and Cable Sizing
- Load Calculations: Determining the total power required by all electrical appliances and equipment in the building. This involves factoring in individual equipment ratings, operating times, and diversity factors.
- Cable Sizing: Selecting the appropriate cable size based on the calculated load, current carrying capacity, voltage drop limitations, and safety codes.
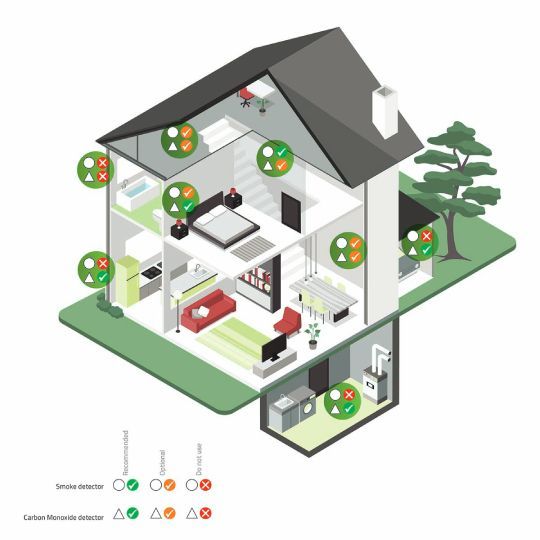
CCTV & Fire Alarm System
- CCTV System Design: Determining the camera locations, cabling requirements, power supply, and recording equipment for a comprehensive security system.
- Fire Alarm System Design: Specifying the placement of smoke detectors, heat sensors, alarm devices, and emergency call points for a reliable fire protection system.
Telephone and Data Layout
- Telecommunication Cabling: Planning the network infrastructure for phone lines and data cables, including conduits, boxes, and connection points.
- Data Network Design: Selecting appropriate equipment and configurations for a robust and secure data network, including routers, switches, and access points.
Transformer Sizing
- Transformer Selection: Determining the necessary capacity and characteristics of the transformer based on the total building load and incoming voltage.
- Placement and Installation: Specifying the location and mounting requirements for the transformer, considering access, cooling, and safety regulations.
Fault Calculations and Protection System Design
- Fault Analysis: Calculating potential short-circuit currents and their impact on electrical components.
- Protection System Design: Selecting and configuring circuit breakers, fuses, and other protective devices to safely isolate faults and prevent damage.
Transformer Sizing (Redundancy)
- This may be a duplicate point, or it could indicate the need for an additional transformer for backup or redundancy purposes, ensuring continued operation in case of primary transformer failure.
These are just brief explanations of each point. Depending on the specific project and your service offerings, each of these areas may involve detailed calculations, equipment selection, and compliance with relevant electrical codes and safety standards.
a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o - Do not remove from template!!! it is important to support different fonts
All Rights Reserved | things-access.com
© 2024